We value your privacy
We use cookies to enhance your browsing experience, serve personalized ads or content, and analyze our traffic. By clicking "Accept All", you consent to our use of cookies.
We use cookies to help you navigate efficiently and perform certain functions. You will find detailed information about all cookies under each consent category below.
The cookies that are categorized as "Necessary" are stored on your browser as they are essential for enabling the basic functionalities of the site. ...
Necessary cookies are required to enable the basic features of this site, such as providing secure log-in or adjusting your consent preferences. These cookies do not store any personally identifiable data.
No cookies to display.
Functional cookies help perform certain functionalities like sharing the content of the website on social media platforms, collecting feedback, and other third-party features.
No cookies to display.
Analytical cookies are used to understand how visitors interact with the website. These cookies help provide information on metrics such as the number of visitors, bounce rate, traffic source, etc.
No cookies to display.
Performance cookies are used to understand and analyze the key performance indexes of the website which helps in delivering a better user experience for the visitors.
No cookies to display.
Advertisement cookies are used to provide visitors with customized advertisements based on the pages you visited previously and to analyze the effectiveness of the ad campaigns.
No cookies to display.

Effective project oversight and control are essential to ensure that initiatives stay on track, meet deadlines, and align with strategic goals. In fast-paced work environments, juggling multiple teams, deadlines, documents, and communications can be overwhelming without the right system. That’s where SharePoint software management comes in as a powerful ally.

The UK’s economic landscape sparkles with opportunity—from London’s global finance hubs to Leeds’ digital corridors and Glasgow’s thriving creative industries. Whether you’re an entrepreneur from Nigeria launching a fintech startup

Email marketing remains one of the most effective digital channels, offering high ROI and personalized reach. But while most marketers focus on subject lines, timing, and content, many overlook a small but powerful element: the link. Specifically, the branded link.

ถ้าคุณกำลังมองหาสินค้า เวชภัณฑ์ความงาม คุณภาพดี ราคาย่อมเยา ที่ 44Botox.com ค้นหาซื้อ 44Botox ผลิตภัณฑ์เวชภัณฑ์ ความงามออนไลน์ อันดับ 1 ราคาส่ง มีสินค้าหลากหลายประเภท ครบทุกความต้องการ ความสวยความงาม.

Hybrid solar systems are the future of residential energy. With benefits like backup power, energy savings, and smart tech integration, they offer unbeatable value in 2025. Whether you’re building a new home or upgrading your current energy setup, investing in a hybrid solar solution is a smart move.

Express your Irvine brand uniquely! Discover how custom metal signs from a local Irvine sign shop offer endless creative possibilities for memorable branding. In the vibrant and competitive business environment
Why More People Are Switching to Solar in 2025 (And How to Find the Right Installer)

Hautpflege ist weit mehr als nur ein ästhetisches Bedürfnis; sie ist ein wichtiger Bestandteil der Gesundheit und des Wohlbefindens. Die richtige Pflege schützt die Haut vor schädlichen Umwelteinflüssen, unterstützt ihre

Get top-tier mobile detailing in Surrey with Las Bespoke Surrey BC. Convenient, professional, and reliable service at your doorstep.

Is your home window tint bubbling, peeling, or outdated? Learn how to safely remove and replace window film on your San Antonio home’s windows. This step-by-step guide covers everything from tools and techniques to the benefits of modern tinting solutions — plus when it’s time to call in the pros for flawless results.
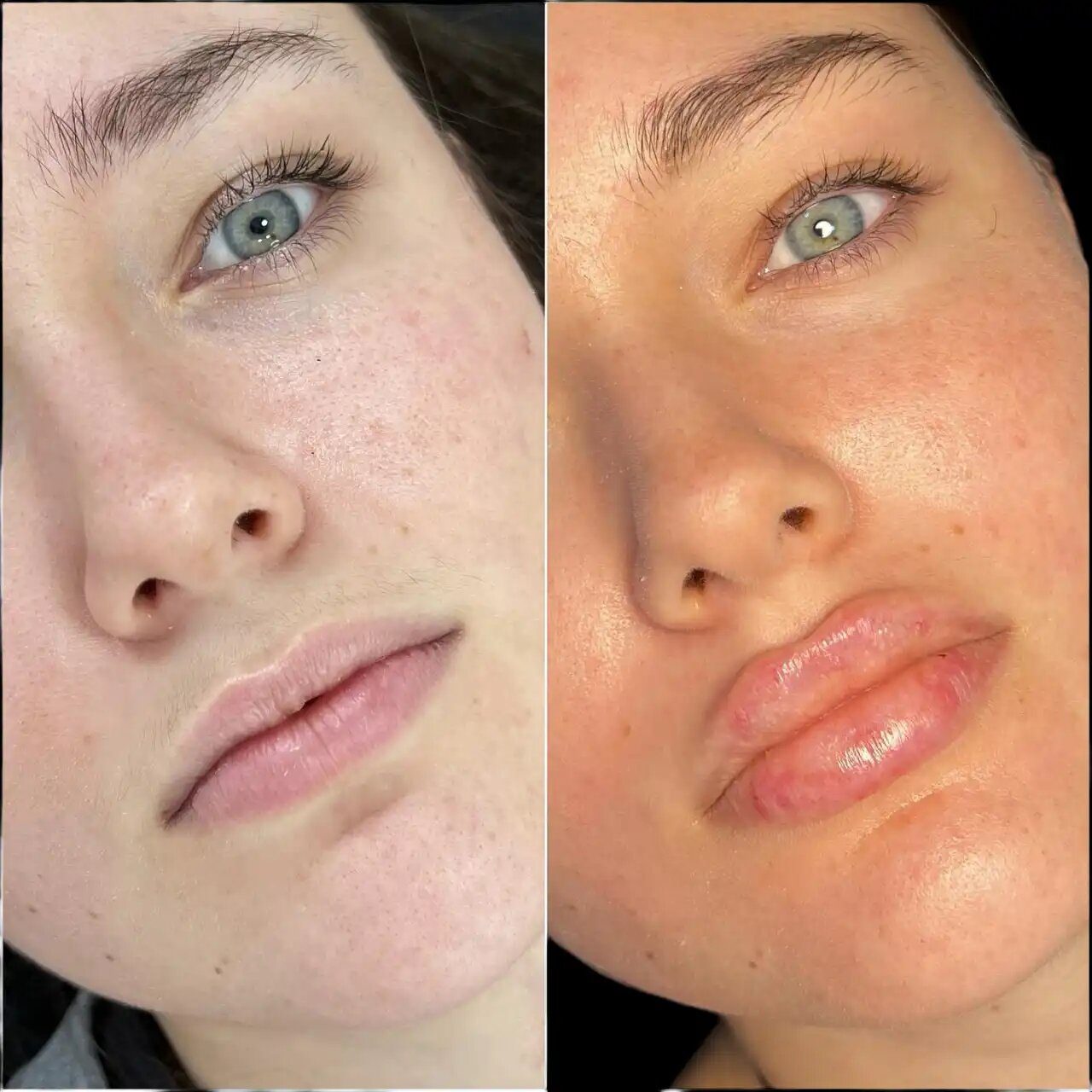
Facial contouring is a popular procedure among individuals looking to enhance their facial features, improve symmetry, and achieve a more youthful appearance. Fillers in Dubai have emerged as a non-surgical

When it comes to celebrating with fireworks, there’s nothing quite as enchanting as Catherine Wheels lighting up the night sky with their fiery spins. Add that to the buzzing atmosphere of the Dartford Fireworks display, and you’ve got yourself a magical evening filled with wonder, tradition, and joy. Whether you’re a fireworks enthusiast, a family looking for a memorable outing, or someone searching for the perfect way to celebrate a special occasion, this guide will walk you through everything you need to know about The Catherine Wheels and the beloved Dartford Fireworks.

In the vibrant heart of India’s capital, the beauty and aesthetics industry is flourishing, driven by growing consumer demand and evolving standards of self-care. Among the many professional skills gaining
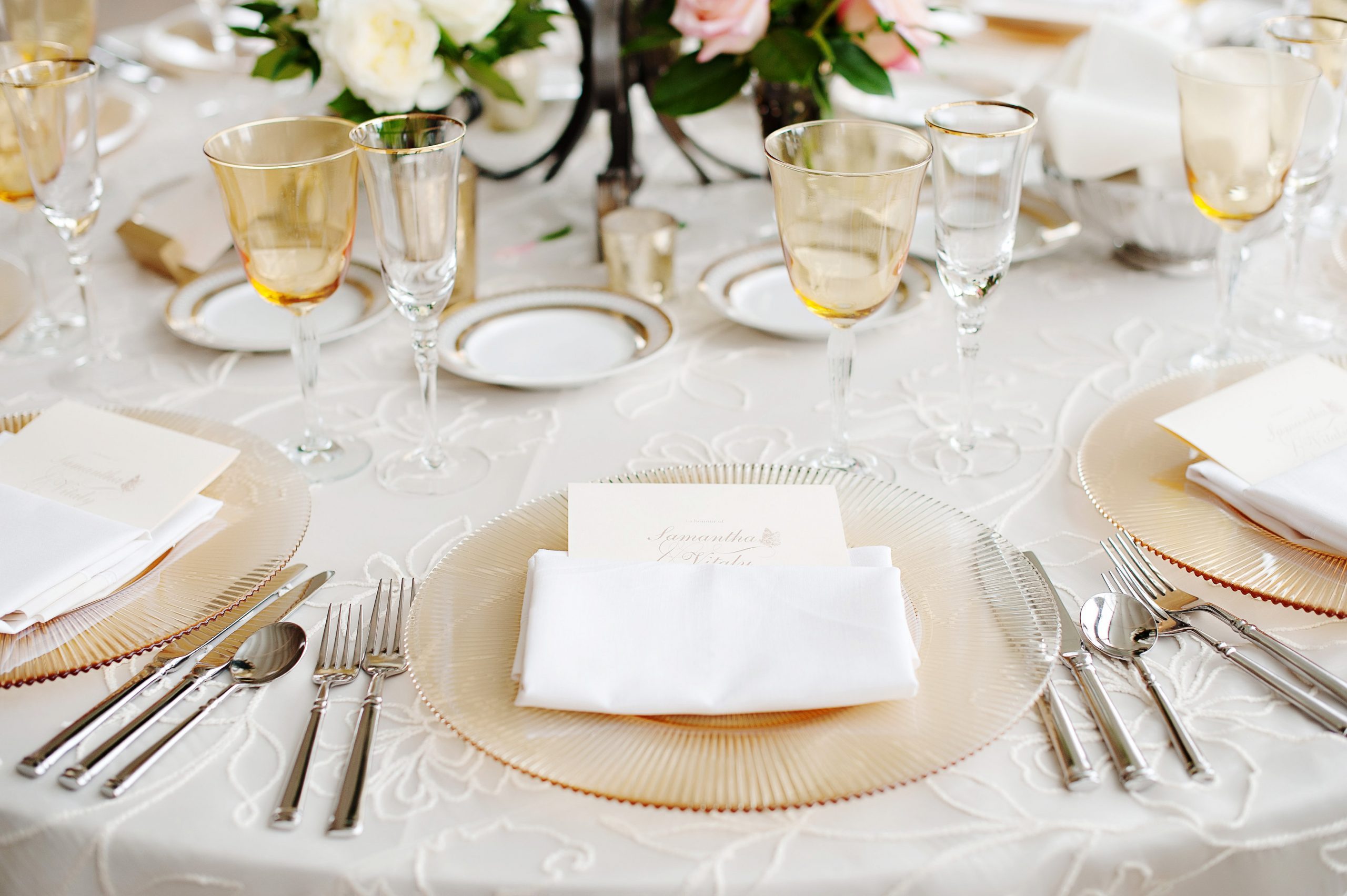

Table settings are an essential aspect of creating the right atmosphere at any event, whether it’s a formal wedding, a corporate gala, or a casual dinner party. One item that

The Parent Visa Subclass 103 allows parents of Australian residents to live in Australia permanently. Though affordable, it has long processing times. The aged version suits seniors already in Australia.

Learn how business intelligence analytics and BI services help optimize supply chain processes, enhance visibility, and improve decision-making.

The Changing Landscape of Work The way we work has evolved dramatically in recent years. As businesses embrace digital tools and employees seek more flexibility, the traditional office environment is

When you think about web design, you probably picture stunning layouts, bold typography, and responsive interfaces. But behind every seamless experience is a web of strategic decisions. Among the most

In today’s competitive food industry, retailers need a reliable and cost-effective source for their inventory. Wholesale food distributors are the backbone of the supply chain, helping businesses maintain consistent stock,

Organic pumpkin seeds are a natural powerhouse for blood sugar management, packed with magnesium, fiber, and healthy fats that improve insulin sensitivity and slow glucose absorption. Their antioxidants also protect against diabetes-related oxidative damage. Enjoy them raw or roasted in meals, snacks, or smoothies for steady energy. For optimal quality, choose certified organic seeds and store them properly.




















Ranks rocket connects website owners with bloggers for free guest posting! Increase brand awareness and backlinks with strategic placements. But remember, quality content is key.