
When it comes to plumber sherwood park services, look no further than Kingstree Plumbing. Our team of licensed and experienced plumbers is dedicated to providing exceptional plumbing solutions to residential and commercial customers in the area.

Mounjaro injections, it’s essential to consult with a qualified healthcare provider to determine if this medication is right for you. With the right medical guidance and lifestyle adjustments, Mounjaro can be a transformative solution to improving your health and quality of life.
In this article, we’ve compiled 20 health tips for students that focus on physical, mental, and emotional well-being

Mavelikara, a serene town nestled in the Alappuzha district of Kerala, has experienced a transformation in its real estate sector over the last few years. This town, which was once

Kohinoor Bhugaon Pune offers premium 2, 3, and 4 BHK Apartments located on Paud Road, Pune. Developed by Kohinoor Developers, the project features spacious units ranging from 794 sq.ft. to 1541 sq.ft., with prices starting at ₹ 79.00 L. The development promises modern amenities, quality, and a serene living experience.

Explore the key differences between Stussy hoodies and Stussy pants, including style, materials, and how to style them for the perfect streetwear look.

La location de voiture à Agadir et son aéroport Al Massira est une option pratique qui vous permettra de profiter pleinement de votre séjour.
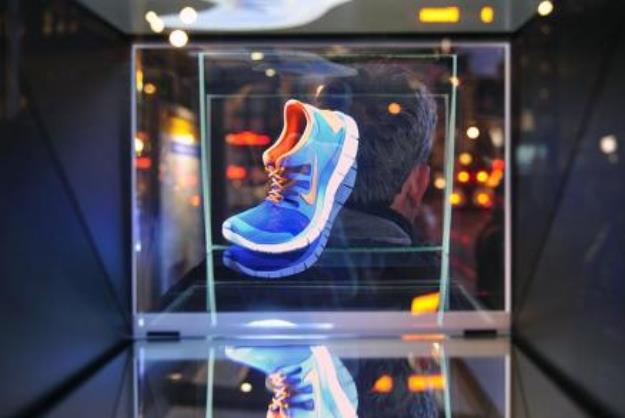

Holographic advertising represents a transformative shift in the way brands capture and engage their audience. By leveraging immersive visuals, interactivity, and enhanced brand recall, holographic ads offer a unique and effective alternative to traditional media.

Facing a visa rejection can be a frustrating and stressful experience. However, the UK immigration system provides avenues to challenge unfair or incorrect decisions through either Administrative Review or Judicial Review.

The Unilevel MLM plan is an effective and flexible compensation structure for businesses in direct selling.

In today’s industrial and commercial sectors, the need for efficient storage and transport solutions is more critical than ever. Whether it’s agricultural products, construction materials, chemicals, or food-grade commodities, businesses
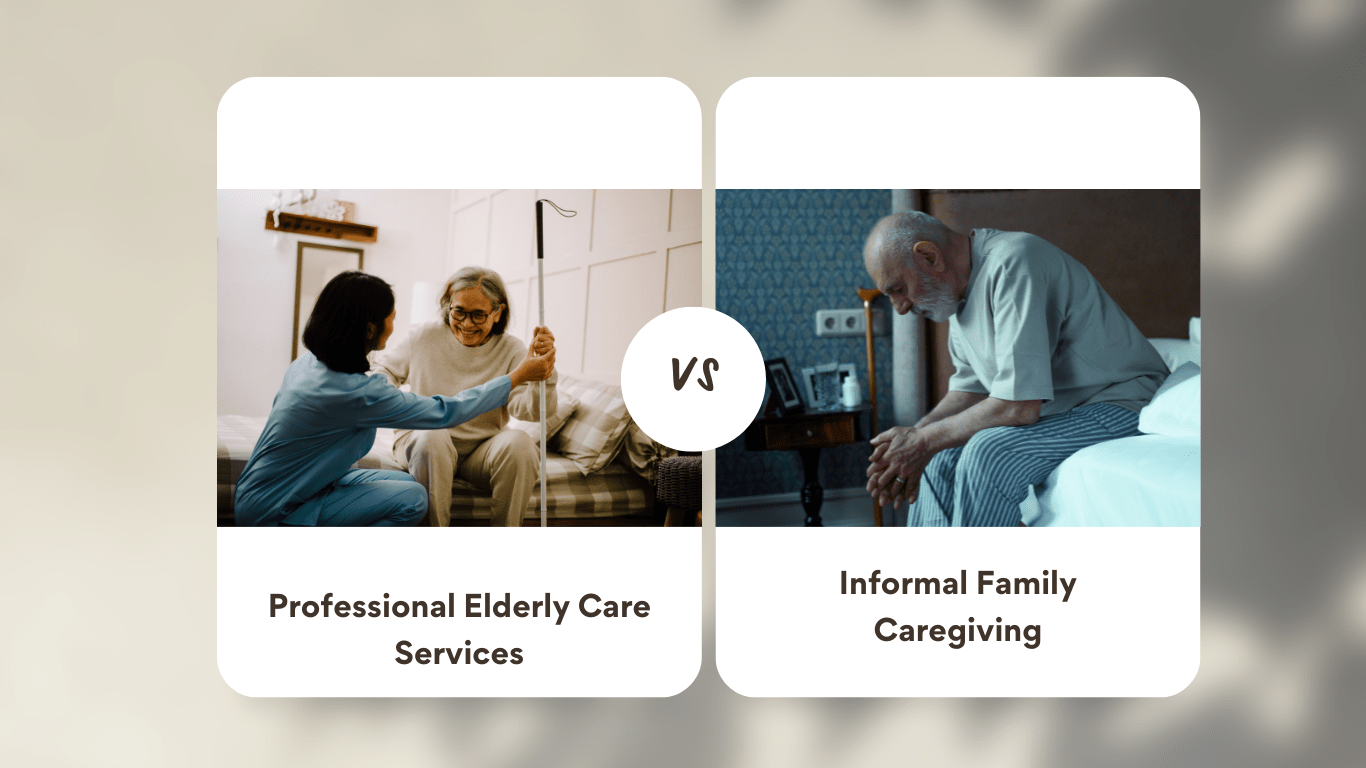
Learn how professional elder care services and family caregiving differ. Choose the best care plan for your elderly loved ones.

The IPMAT exam is a highly competitive entrance test for aspirants seeking admission to the prestigious five-year Integrated Program in Management offered by institutions like IIM Indore and IIM Rohtak.

The post basic B.Sc. Nursing is a course for registered nurses who upgrade their skills and grow in their careers. The program includes advanced nursing practices, leadership development, and hands-on
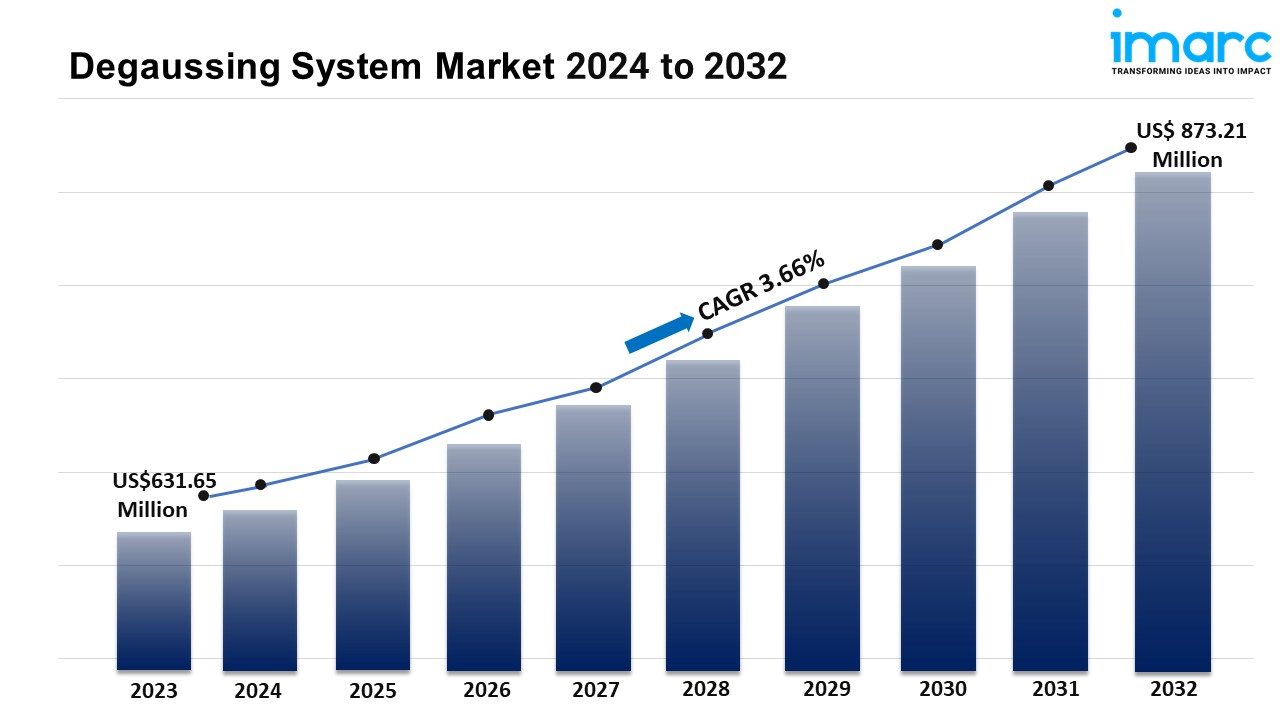
The global degaussing system market size reached US$ 631.65 Million in 2023. Looking forward, IMARC Group expects the market to reach US$ 873.21 Million by 2032, exhibiting a growth rate (CAGR) of 3.66% during 2024-2032.

The Primary School Leaving Examination (PSLE) marks a significant phase in a child’s educational journey in Singapore. With its revamped scoring system, the PSLE now places greater emphasis on individual

Discover how to become a certified barista in Perth. Explore courses, costs, demand, and career opportunities in Australia’s thriving coffee industry.

Cannabis legalization has evolved globally, shifting from widespread criminalization to growing acceptance. Countries like Canada and Uruguay have led the way, with many others considering or implementing reforms due to medical benefits, social justice, and public support.
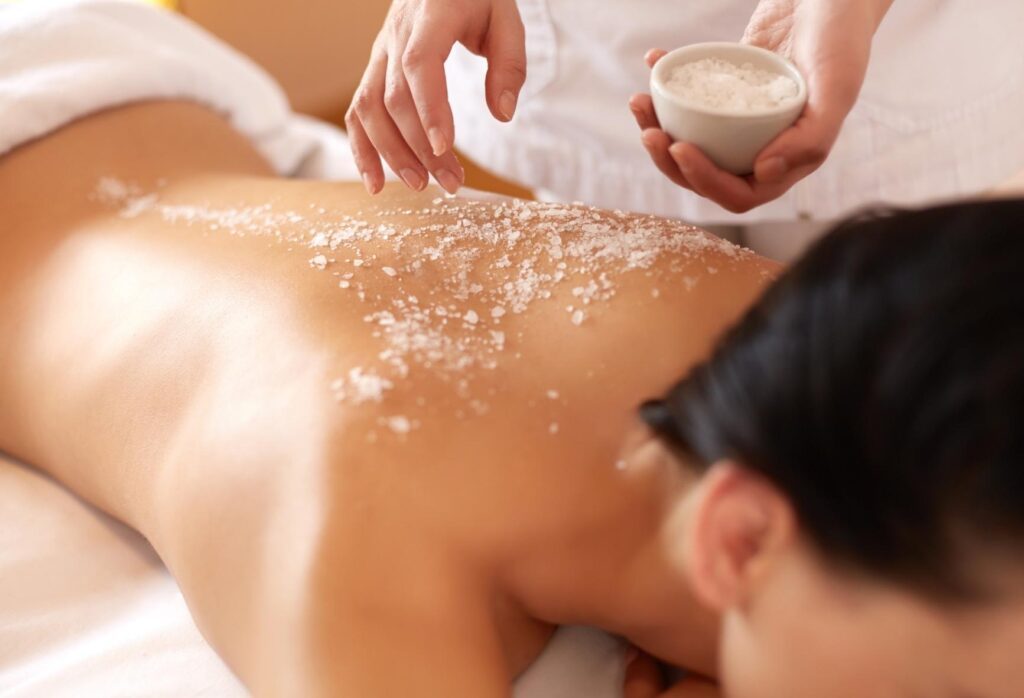

Travelers are offered a serene wellness retreat with therapies like Shirodhara, a soothing Ayurvedic treatment for erasing all stress, enhancing sleep, and increasing mental clarity. Salt & Aroma, an offering of Panchtatva Gurnani, aims to provide such relaxation to its clients with expert therapists, personalized programs, and an ambiance that brings one close to nature. Visit https://panchtatvagurnani.com/ to plan your wellness journey.

Running a business around the world opens up exciting chances. It helps companies sell more products, meet new customers, and earn more money. International shipping services make this all possible.




















Ranks rocket connects website owners with bloggers for free guest posting! Increase brand awareness and backlinks with strategic placements. But remember, quality content is key.