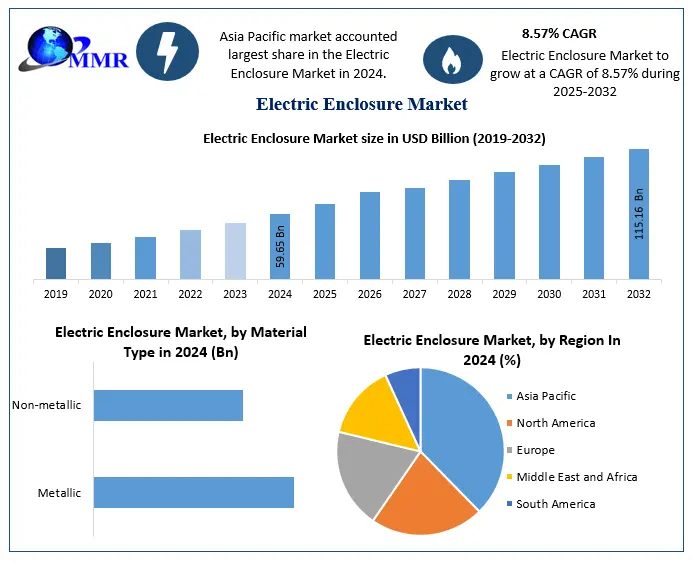
Hydraulic fittings are essential components in fluid power systems. These fittings serve a critical purpose in connecting and sealing hydraulic hoses, pipes, and tubes. They are used in various industries, from construction and agriculture to manufacturing and automotive. Understanding hydraulic fittings and their role in fluid power systems is key to ensuring the performance, safety, and longevity of these systems.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore everything you need to know about hydraulic fittings, from their types and materials to their functions and applications. We will also highlight best practices for selecting, installing, and maintaining these crucial components.
What Are Hydraulic Fittings?
Hydraulic fittings are connectors used to link various parts of a hydraulic system, including pipes, hoses, and tubes. They facilitate the transmission of hydraulic fluid throughout the system. These fittings ensure that fluid flows smoothly and without leakage, which is crucial in high-pressure environments where even small leaks can lead to inefficiencies and safety risks.
Hydraulic fittings are designed to withstand high pressures, extreme temperatures, and harsh environments. They play a vital role in preventing fluid loss, maintaining pressure levels, and ensuring system stability.
Types of Hydraulic Fittings
There are several types of hydraulic fittings, each designed to serve a specific function. The most common types include:
-
Compression Fittings: These fittings are used to connect tubes or pipes to other components in the system. They provide a tight seal by compressing a ferrule around the tube as the fitting is tightened. This type of fitting is ideal for applications where the pipe or tube needs to be connected to a system without threading.
-
Threaded Fittings: These are among the most common types of hydraulic fittings. They feature internal or external threads that allow them to be screwed into place. Threaded fittings come in various types, including NPT (National Pipe Thread), BSP (British Standard Pipe), and SAE (Society of Automotive Engineers) threads.
-
Flared Fittings: These fittings are used when a tube needs to be connected to a fitting by flaring the end of the tube. The flare forms a tight seal that can withstand high pressures. Flared fittings are commonly used in applications involving gas or high-pressure fluid transfer.
-
Quick Connect Fittings: As the name suggests, quick-connect fittings allow for easy and fast connection and disconnection of hoses, pipes, and other system components. These fittings are often used in mobile equipment or systems that require frequent assembly and disassembly.
-
Barbed Fittings: These fittings have a barbed design that grips onto the inner surface of the hose to ensure a secure connection. Barbed fittings are often used in low-pressure applications and are ideal for flexible hoses.
-
Push-to-Connect Fittings: These fittings are designed to connect quickly by simply pushing a tube or hose into the fitting. Once inserted, the fitting locks in place, creating a tight seal without the need for additional tools or equipment.
Materials Used for Hydraulic Fittings
Hydraulic fittings are made from a variety of materials, each selected for its ability to withstand high pressures, extreme temperatures, and corrosive environments. The most common materials used for hydraulic fittings include:
-
Steel: Steel is the most widely used material for hydraulic fittings. It is durable, corrosion-resistant, and capable of handling high-pressure applications. Stainless steel, in particular, is favored for its resistance to corrosion in harsh environments.
-
Brass: Brass is commonly used in hydraulic fittings due to its corrosion resistance and ease of machining. It is often used in low-pressure systems and in applications where aesthetics are important.
-
Aluminum: Aluminum hydraulic fittings are lightweight and resistant to corrosion. They are ideal for applications where weight is a concern, such as in aerospace or automotive systems.
-
Plastic: Some hydraulic fittings are made from high-strength plastics, such as polyamide and polypropylene. These are used in low-pressure applications and are ideal for systems that do not require the durability of metal fittings.
Functions of Hydraulic Fittings
The primary function of hydraulic fittings is to connect components within a hydraulic system. However, their role extends beyond just physical connection. Some of the key functions of hydraulic fittings include:
-
Sealing: One of the most important functions of hydraulic fittings is to prevent leakage. A well-sealed hydraulic fitting ensures that fluid remains contained within the system, preventing contamination and loss of pressure.
-
Pressure Maintenance: Hydraulic fittings play a key role in maintaining the pressure within a hydraulic system. By creating tight seals, they help prevent fluid from escaping, which would result in a drop in pressure.
-
Fluid Flow Control: Hydraulic fittings can help control the flow of fluid within a system. By choosing the right type of fitting for a specific application, engineers can ensure that fluid flows smoothly and efficiently.
-
Adaptation: Some hydraulic fittings are used to adapt one type of connection to another. For example, a fitting might convert a threaded connection to a flared connection, allowing for greater flexibility in system design.
Applications of Hydraulic Fittings
Hydraulic fittings are used in a wide range of applications across various industries. Some of the most common applications include:
-
Construction: Hydraulic systems are widely used in construction equipment, such as cranes, excavators, and bulldozers. Hydraulic fittings ensure the smooth operation of these machines by connecting various hydraulic components.
-
Automotive: Hydraulic fittings are used in the automotive industry in applications such as braking systems, power steering, and suspension systems. These fittings help ensure the reliability and performance of these critical systems.
-
Aerospace: In the aerospace industry, hydraulic systems are used in aircraft controls, landing gear, and other vital systems. The reliability of hydraulic fittings is crucial in these high-pressure environments.
-
Agriculture: Hydraulic systems are commonly used in agricultural equipment, such as tractors, harvesters, and irrigation systems. Hydraulic fittings help ensure the efficient operation of these machines.
-
Manufacturing: In manufacturing plants, hydraulic systems are used for presses, lifts, and other machinery. Hydraulic fittings are essential for maintaining the pressure and flow of fluid within these systems.
How to Choose the Right Hydraulic Fittings
Selecting the right hydraulic fittings is crucial to ensuring the efficiency and safety of a hydraulic system. When choosing hydraulic fittings, consider the following factors:
1. Compatibility with Materials
Ensure that the hydraulic fittings are compatible with the materials used in the system. For example, if your system uses aluminum tubes, ensure that the fittings are compatible with aluminum to prevent corrosion or damage to the components.
2. Pressure Rating
Check the pressure rating of the hydraulic fittings to ensure they can withstand the maximum pressure your system will experience. Using fittings that cannot handle the required pressure could lead to failure and system downtime.
3. Temperature Resistance
Consider the temperature range of the hydraulic system and choose fittings that can operate within this range. Some hydraulic systems operate at extremely high or low temperatures, and choosing fittings that cannot handle these conditions can lead to performance issues or failure.
4. Seal Type
Different hydraulic fittings use different types of seals to prevent leakage. The most common seal types include O-rings, gasket seals, and metal-to-metal seals. Choose the appropriate seal type based on the fluid type, pressure, and temperature of your system.
5. Ease of Installation
Consider the ease of installation when selecting hydraulic fittings. Some fittings, such as quick-connect fittings, can be installed quickly without special tools, while others, such as flared fittings, require more effort and expertise.
6. Corrosion Resistance
For systems operating in corrosive environments, such as those exposed to chemicals or saltwater, choose hydraulic fittings made from corrosion-resistant materials like stainless steel or plastic.
7. Cost and Quality
While it is important to select high-quality hydraulic fittings, cost considerations are also important. Balancing cost and quality is crucial to ensuring the long-term reliability and cost-effectiveness of the system.
Best Practices for Installing Hydraulic Fittings
Proper installation of hydraulic fittings is essential to ensure their performance and prevent leaks. Here are some best practices for installing hydraulic fittings:
-
Cleanliness: Ensure that all components, including hydraulic hoses, tubes, and fittings, are clean before installation. Dirt or debris can damage seals and lead to leaks.
-
Correct Torque: Apply the correct amount of torque when tightening hydraulic fittings. Over-tightening can damage the fitting, while under-tightening can lead to leaks.
-
Inspect Seals: Check the seals on hydraulic fittings before installation to ensure they are in good condition. Replace any damaged or worn seals to prevent leaks.
-
Use the Right Tools: Use the appropriate tools for installing hydraulic fittings, such as wrenches and torque tools. Avoid using makeshift tools that could damage the fittings.
-
Proper Alignment: Ensure that all components are properly aligned before tightening the fittings. Misalignment can cause stress on the fittings and lead to premature failure.
Common Issues with Hydraulic Fittings and How to Address Them
Despite their durability, hydraulic fittings can encounter issues over time. Some common issues include:
-
Leaks: Leaks are one of the most common problems with hydraulic fittings. To prevent leaks, ensure that the fittings are properly tightened, and that the seals are in good condition.
-
Corrosion: Corrosion can occur when hydraulic fittings are exposed to harsh environments. To prevent corrosion, select fittings made from corrosion-resistant materials and ensure proper maintenance.
-
Wear and Tear: Over time, hydraulic fittings may experience wear and tear, leading to reduced performance. Regularly inspect fittings for signs of damage and replace any worn components.
-
Wrong Size: Using the wrong size fitting can cause pressure drops, leaks, or system failure. Always ensure that the fittings match the size of the hoses or pipes they are being connected to.
Conclusion
Hydraulic fittings play a crucial role in fluid power systems. By connecting various components, ensuring fluid flow, and maintaining pressure, they help keep hydraulic systems operating smoothly and efficiently. Understanding the types, functions, and applications of hydraulic fittings, along with best practices for selecting and installing them, is essential for ensuring the reliability and longevity of hydraulic systems.