We value your privacy
We use cookies to enhance your browsing experience, serve personalized ads or content, and analyze our traffic. By clicking "Accept All", you consent to our use of cookies.
We use cookies to help you navigate efficiently and perform certain functions. You will find detailed information about all cookies under each consent category below.
The cookies that are categorized as "Necessary" are stored on your browser as they are essential for enabling the basic functionalities of the site. ...
Necessary cookies are required to enable the basic features of this site, such as providing secure log-in or adjusting your consent preferences. These cookies do not store any personally identifiable data.
No cookies to display.
Functional cookies help perform certain functionalities like sharing the content of the website on social media platforms, collecting feedback, and other third-party features.
No cookies to display.
Analytical cookies are used to understand how visitors interact with the website. These cookies help provide information on metrics such as the number of visitors, bounce rate, traffic source, etc.
No cookies to display.
Performance cookies are used to understand and analyze the key performance indexes of the website which helps in delivering a better user experience for the visitors.
No cookies to display.
Advertisement cookies are used to provide visitors with customized advertisements based on the pages you visited previously and to analyze the effectiveness of the ad campaigns.
No cookies to display.
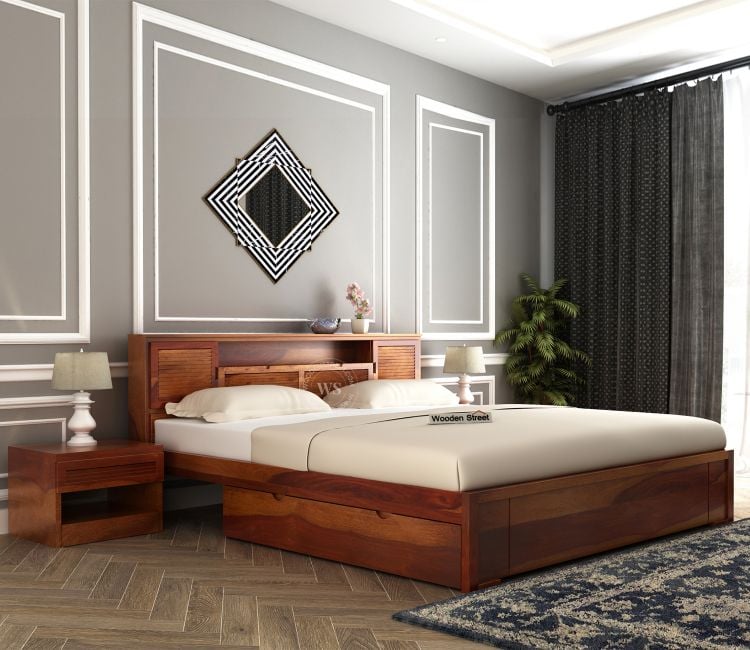

From minimal frames to richly detailed headboards, these inspirations serve as a visual roadmap to upgrade your bedroom in a way that feels fresh, intentional, and uniquely yours.

This blog talks about the best course after 12 for Arts students and the top jobs in India for freshers. After finishing class 12 with Arts, students have many good options like B.A., BFA, BJMC, B.Des, Hotel Management, Law, and Digital Marketing. These courses help students build strong careers in areas they enjoy.

Whether you’re a start-up or an established local brand, investing in small business SEO services and choosing to hire dedicated SEO experts can significantly enhance your online presence, attract qualified leads, and boost your bottom line.

In the dynamic packaging, where aesthetics face flexibility, a material has emerged as a precursor, providing unique clarity and strong protection: biaxally oriented polypropylene, or bop.
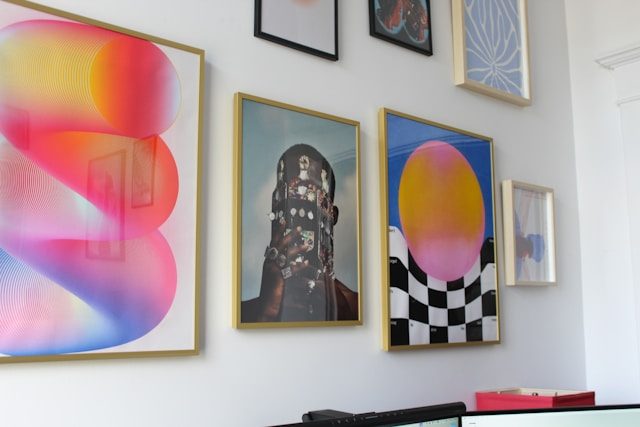

Minimalist wall art is a powerful design choice that emphasizes simplicity, clean lines, and a restrained use of color and form to create serene and sophisticated visual environments.

If you’re passionate about astrology and looking for a logical, precise, and deeply insightful approach, then the KP astrology course at IIAG Jyotish Sansthan is a perfect choice. And with the course now available online, you have the flexibility to learn from anywhere in the world—without missing out on quality instruction or personal guidance. Whether your goal is personal growth or professional advancement, this course will equip you with the knowledge and skills to make accurate predictions and become a respected voice in the astrology community.
Nature has always been a timeless source of design inspiration, and when it comes to interiors, nature wallpaper offers an immersive way to bring the outside world into your living

Discover four key compliance challenges in the financial sector and how Predict360’s AI-powered platform helps institutions streamline operations, reduce risk, and stay ahead of regulatory demands.

Design your dream wedding invite without breaking the bank! Explore wedding invitation templates that are editable, beautiful, and perfect for every wedding theme. Create stunning wedding invites Discover beautiful, editable wedding invitation templates for print or digital use. Start designing today.

Make your move today, partner with the right development team, and drive into the future of urban mobility! https://www.trioangle.com/taxi-app-development/

In recent years, many people have become interested in natural supplements that may support health.

https://app.site123.com/blog/tv-shows-with-bilal-abbas-khan-you-shouldn-t-miss?w=10585243&disableCache=680b6a03121c3 https://aquireacres01.wixsite.com/my-site/post/tv-shows-with-bilal-abbas-khan-you-shouldn-t-miss https://aquireacres01.wordpress.com/2025/04/25/tv-shows-with-bilal-abbas-khan-you-shouldnt-miss/ https://www.tumblr.com/aquireacres01/781791837140713472/tv-shows-with-bilal-abbas-khan-you-shouldnt-miss?source=share https://aquireacres01.mystrikingly.com/blog/tv-shows-with-bilal-abbas-khan-you-shouldn-t-miss https://aquireacres01.blogspot.com/2025/04/tv-shows-with-bilal-abbas-khan-you.html https://medium.com/@aquireacres01/tv-shows-with-bilal-abbas-khan-you-shouldnt-miss-36dfd574a358 https://aarambhhaiprachand.hashnode.dev/from-divine-chants-to-dramatic-cinemas-exploring-indias-spiritual-roots-and-diverse-entertainment-landscape https://writeupcafe.com/Aarambhhaiprachand https://aquireacres01.stck.me/post/1013700/From-Divine-Chants-to-Dramatic-Cinemas-Exploring-Indias-Spiritual-Roots-and-Diverse-Entertainment-Landscape https://www.latinosdelmundo.com/article/from-divine-chants-to-dramatic-cinemas https://www.ranksrocket.com/from-divine-chants-to-dramatic-cinemas-exploring-indias-spiritual-roots-and-diverse-entertainment-landscape/ https://aquireacres01.livejournal.com/349.html https://timessquarereporter.com/others/from-divine-chants-to-dramatic-cinemas--exploring-india-s-spiritual-roots-and-diverse-entertainment-landscape https://graph.org/From-Divine-Chants-to-Dramatic-Cinemas-Exploring-Indias-Spiritual-Roots-and-Diverse-Entertainment-Landscape-05-14-2 https://telegra.ph/From-Divine-Chants-to-Dramatic-Cinemas-Exploring-Indias-Spiritual-Roots-and-Diverse-Entertainment-Landscape-05-14 https://justpaste.it/ath2e https://livepositively.com/from-divine-chants-to-dramatic-cinemas-exploring-indiaaos-spiritual-roots-and-diverse-entertainment-landscape/ https://digital24hour.com/aarambh-hai-prachand-lyrics-and-vakratunda-mahakaya/ https://digital24hour.com/om-namah-parvati-pataye-har-har-mahadev-and-hindu-calendar-2025-a-spiritual-guide-to-the-year-ahead/ https://digital24hour.com/mithe-ras-se-bhari-radha-rani-lage-lyrics-a-divine-tribute-to-radha-ranis-beauty-and-grace/ https://digital24hour.com/korean-adult-movies-and-bollywood-romantic-movies-exploring-two-cinematic-worlds-of-love-passion-and-emotion/ https://digital24hour.com/punjabi-web-series-and-top-10-malayalam-web-series-regional-stories-that-rule-ott/ https://digital24hour.com/kannada-horror-movies-a-spine-chilling-ride-through-sandalwoods-dark-side/

Explore IUI treatment at Ekam Fertility – the best IUI center in Hyderabad. Learn about the IUI treatment procedure, success rate, and why we’re also known as the best IVF clinic in Hyderabad.
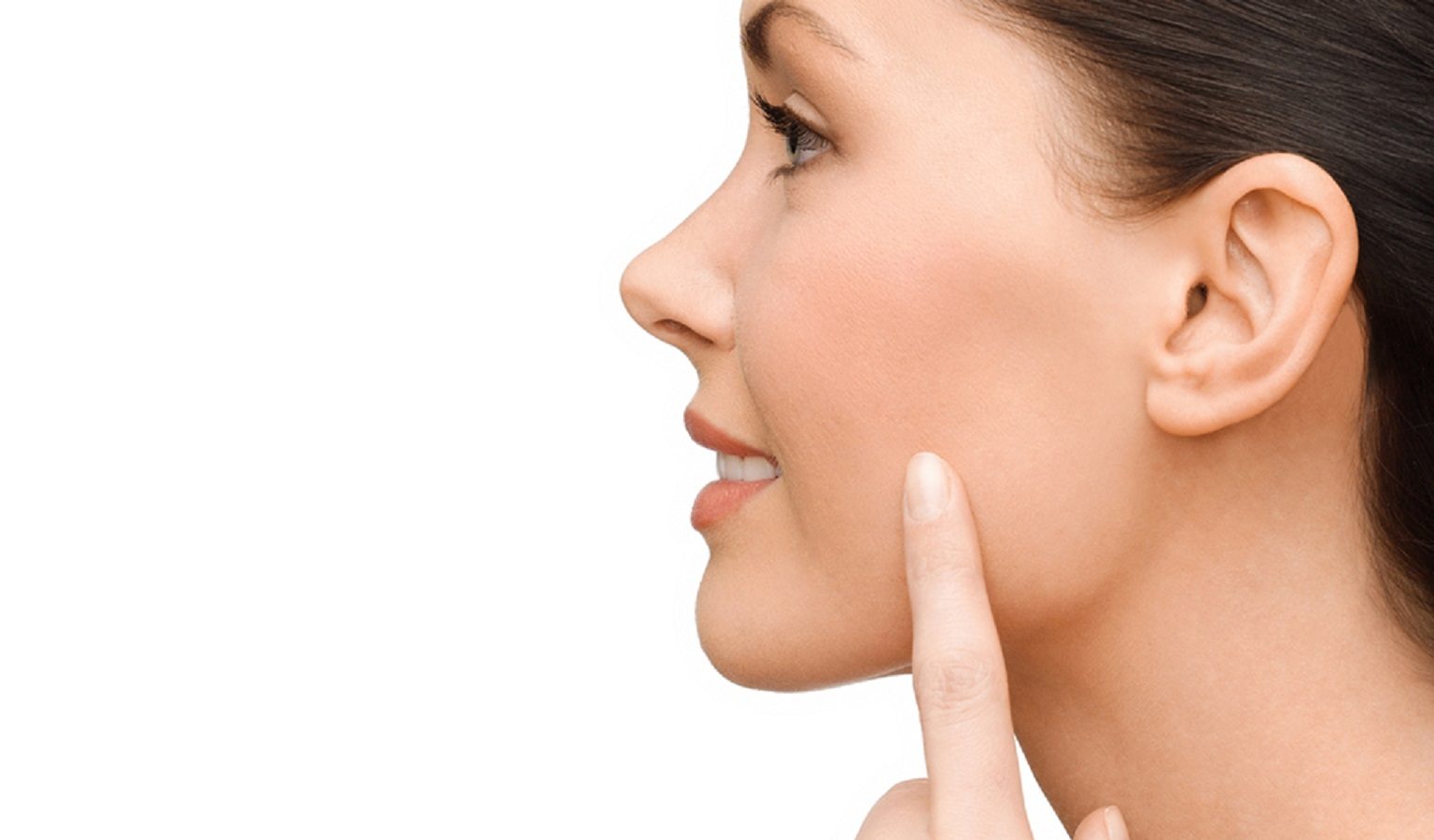

Cheek reduction surgery, also known as buccal fat removal, is a cosmetic procedure designed to reduce the prominence of the cheeks by removing the buccal fat pads located in the lower part of the cheeks. This surgery is especially popular among individuals looking to achieve a more contoured, chiseled facial structure.

Discover practical, proven cost-saving strategies for startups hiring developers. Learn how to build a high-performing dev team
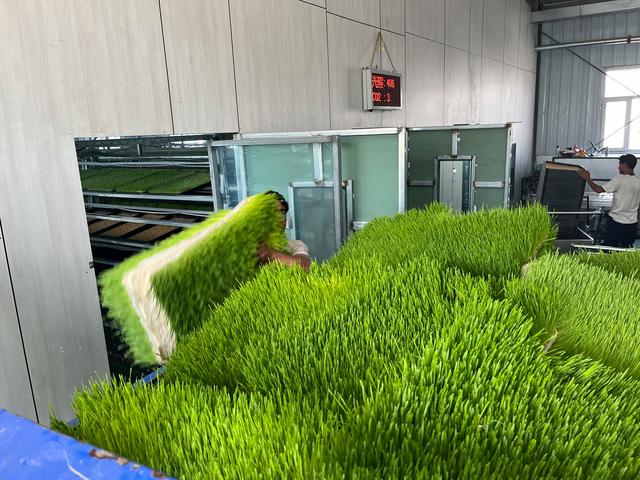

This article explores, in depth, the reality of hydroponic barley fodder’s palatability for cows and sheep, drawing on field experience, academic studies, and the often-overlooked behavioral nuances that drive ruminant feed preferences.

Discover the royal charm of Jaipur with My Trip Planner. Customized tour packages with heritage stays, guided tours, and seamless travel.
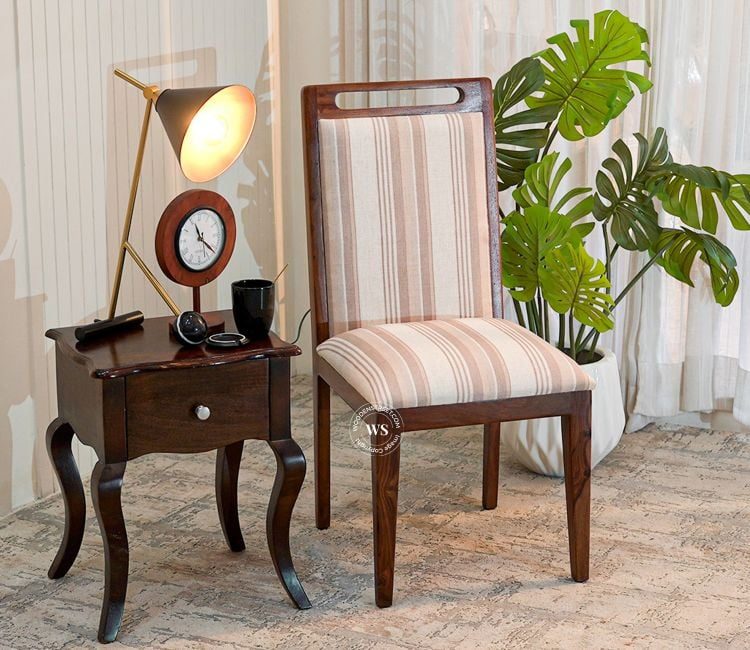

When it comes to dining room furniture, selecting the perfect dining chair height for your table is just as important as choosing the style or material. The height of your
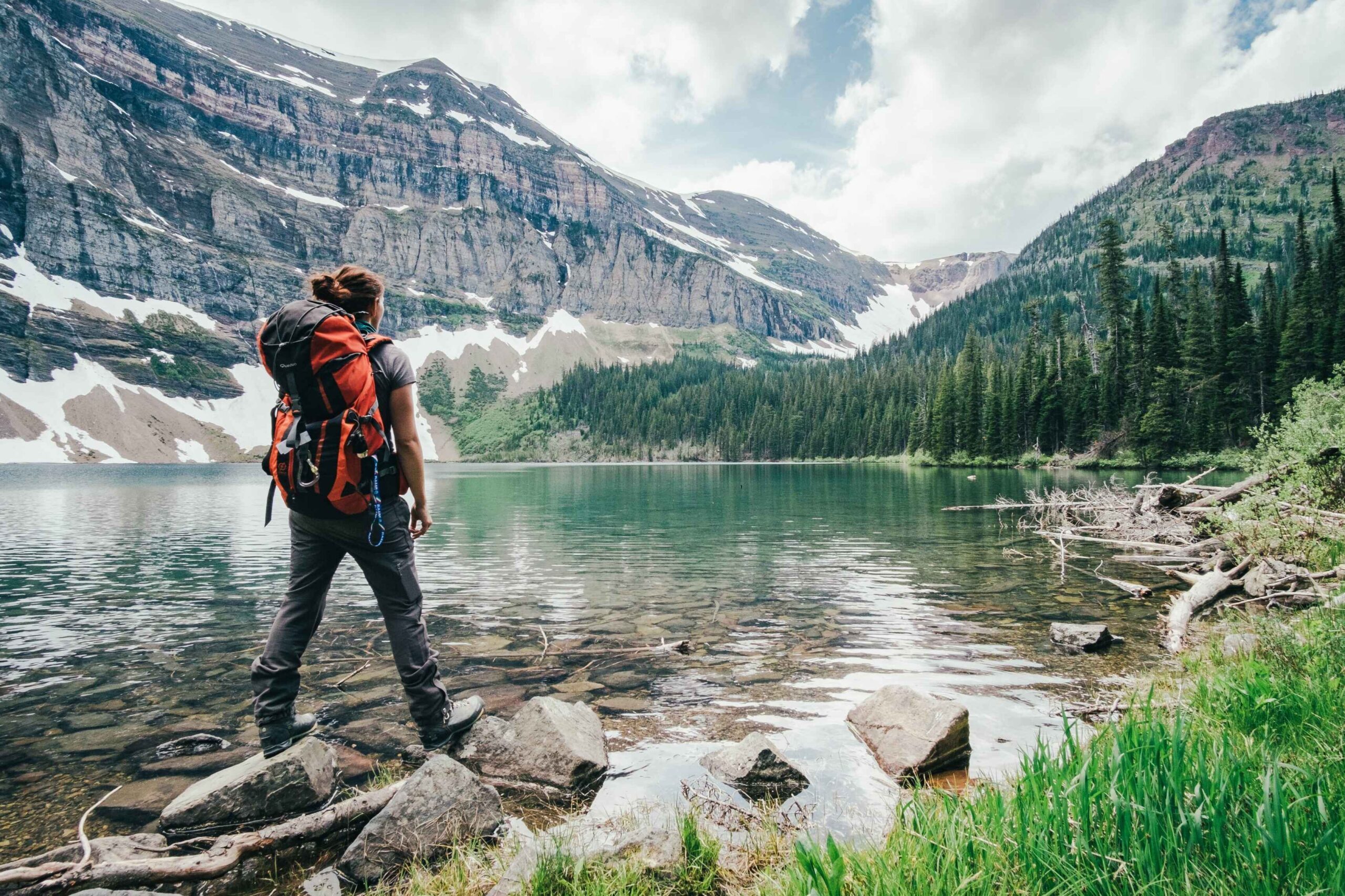

If you're someone who loves fine living, beautiful destinations, and top-class services, then a luxury travel experience is the perfect way to enjoy life. From breathtaking desert dunes to modern
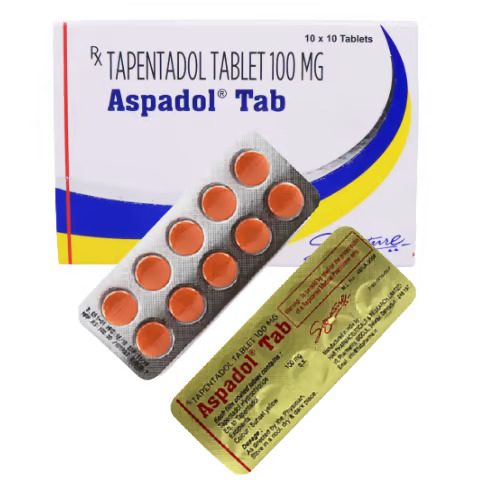
Aspadol 100 mg is a prescription opioid painkiller containing Tapentadol, used to treat moderate to severe pain. It works through dual action—opioid receptor activation and norepinephrine reuptake inhibition. Effective for chronic conditions and post-operative pain, it should be used strictly under medical supervision due to risks of side effects and addiction.



















Ranks rocket connects website owners with bloggers for free guest posting! Increase brand awareness and backlinks with strategic placements. But remember, quality content is key.